
The Infant Skull A Vault of Information RadioGraphics
Patient Positioning for Skull Radiography. Patients can be imaged either erect or recumbent. In the erect position, a standard X-ray table and upright Bucky are used. This allows easy and quick positioning and use of a horizontal beam, which is necessary to demonstrate any air-fluid levels in the cranium or sinuses.
EPOS™
X-rays use a small amount of radiation beams to make images. Standard X-rays are done for many reasons. They are done to diagnose tumors, infection, foreign bodies, or bone injuries. X-ray beams pass through body tissues onto treated plates. The more solid a structure is, the whiter it appears on the film.
Infant Skull Xray Photograph by Photo Researchers Pixels
While somewhat gnarly, sure, but it's still rather fascinating to see what it looks like as permanent teeth form within the skull before pushing out baby teeth. Below, a time-lapse video of permanent teeth growing in:

Massive congenital depression of neonate’s skull ADC Fetal & Neonatal Edition
A skull X-ray is a series of pictures of the bones of the skull. Skull X-rays have largely been replaced by computed tomography (CT) scans. A skull X-ray may help find head injuries, bone fractures, or abnormal growths or changes in bone structure or size. The bones of the skull are normal in size and appearance.

A MonthOld Infant Misdiagnosed with Child Abuse
Definition. A skull x-ray is a picture of the bones surrounding the brain, including the facial bones, the nose, and the sinuses.. Alternative Names. X-ray - head; X-ray - skull; Skull radiography; Head x-ray. How the Test is Performed. You lie on the x-ray table or sit in a chair.

X Ray Della Vista Laterale Del Cranio Umano Del Bambino Fotografia Stock Immagine di umano
Indications. This examination is able to assess for medial and lateral displacements of skull fractures, in addition to neoplastic changes and Paget disease. Note: As this view results in higher radiation dose to the radiosensitive lens of the eyes compared to the PA view, it should only be used in situations where the patient is unable to face.

The Infant Skull A Vault of Information RadioGraphics
Sinus infection ( sinusitis) Sometimes skull x-rays are used to screen for foreign bodies that may interfere with other tests, such as an MRI scan. A CT scan of the head is usually preferred to a skull x-ray to evaluate most head injuries or brain disorders. Skull x-rays are rarely used as the main test to diagnose such conditions.

The Infant Skull A Vault of Information RadioGraphics
Aim: To determine optimal exposure parameters when performing digital skull radiographs in infants with suspected non-accidental injury (NAI). Method: Anteroposterior and lateral post-mortem skull radiographs of six consecutive infants with suspected NAI were made at six exposure levels for each projection. Entrance surface doses ranged from 75-351 microGy.

how do they xray babies head Misha Cowart
Bickle I, Normal AP skull radiograph - pediatric. Case study, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 13 Dec 2023) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-46691

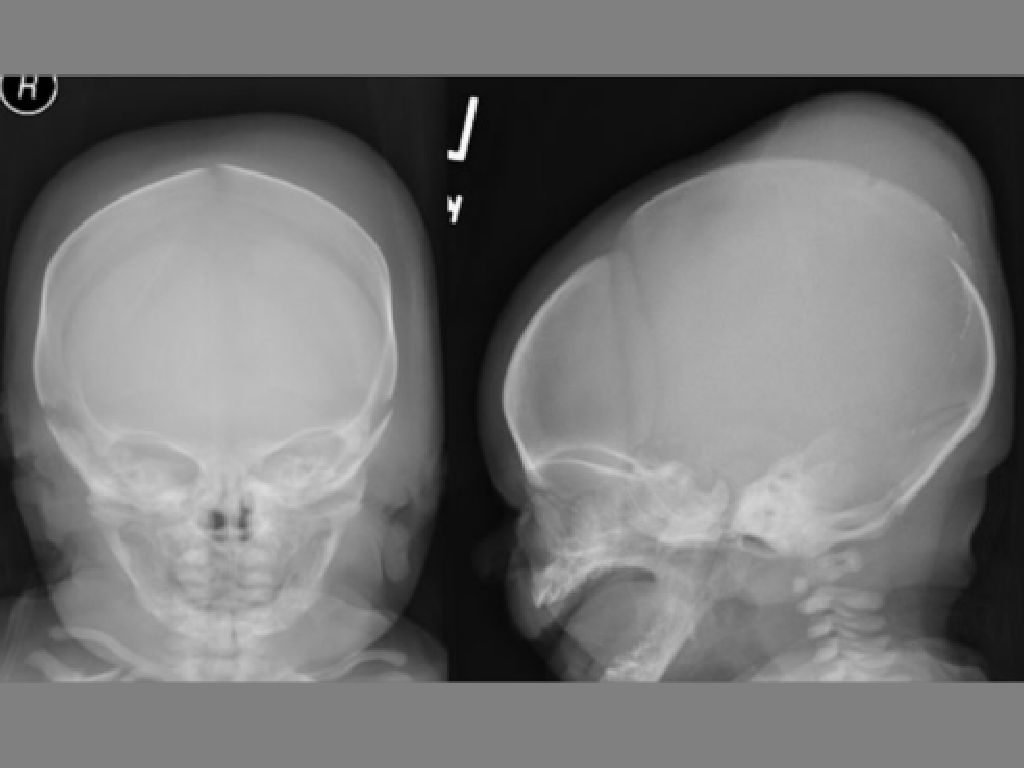
Lateral skull xray in a 4 month old male. The skull is scaphocephalic... Download Scientific
Introduction. Skull lesions in the paediatric population are common entities and often constitute a diagnostic dilemma for radiologists. A wide spectrum of lesions exists, which includes congenital, traumatic, infectious, neoplastic, vascular, and post-surgical abnormalities during imaging pathways.
Skull xray
Ultrasound. hip : figure 1 example normal-pediatric- hip-ultrasound-graf-type-i. Skeletal survey. Skeletal surveys are performed in cases of:. suspected non-accidental pediatric skeletal injury. 1-month-old: example 1 5-month-old: example 1 post-mortem before an autopsy in cases of suspected sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) to exclude traumatic skeletal injury or skeletal abnormalities.

Skull Fracture in an Infant Not Visible with Computed Tomography The Journal of Pediatrics
The art of interpreting skull radiographs is slowly being lost as trainees in radiology see fewer plain radiographs and depend more heavily on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Nevertheless, skull radiographs still provide significant information that is helpful in finding pathologic conditions and appreciating their extents. Abnormalities in the skull may be reflected as.
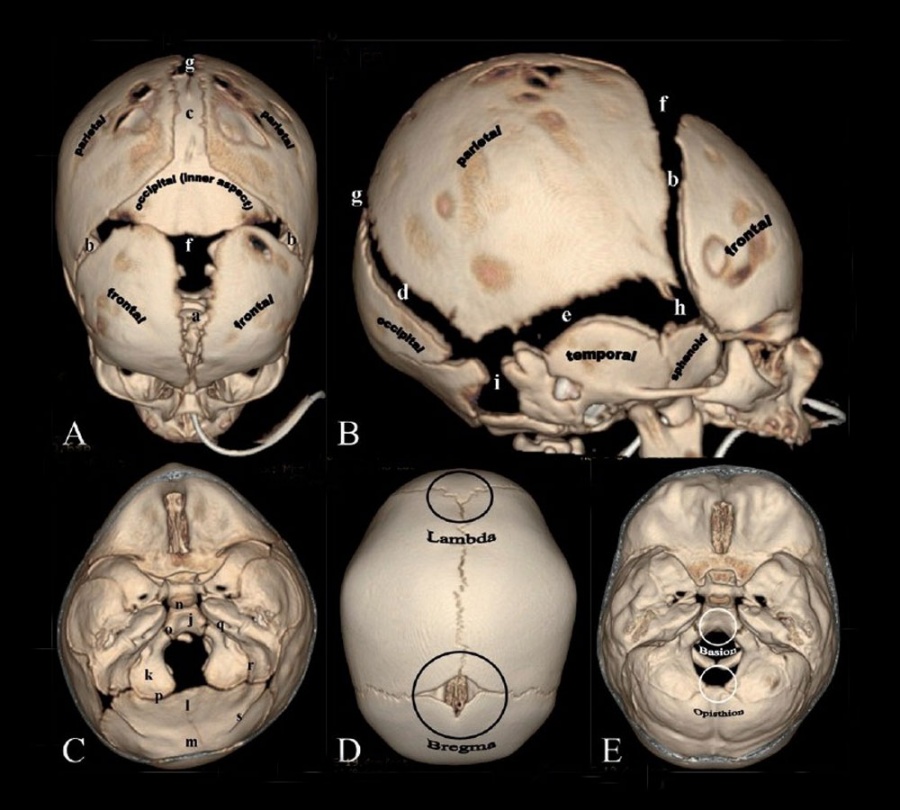
Neural Exam Newborn head shape and sutures Embryology
Skull radiography is the radiological investigation of the skull vault and associated bony structures. Seldom requested in modern medicine, plain radiography of the skull is often the last resort in trauma imaging in the absence of a CT.

The Infant Skull A Vault of Information RadioGraphics
Scoliosis films: PA thoracolumbar spines from iliac crests to cervical spine. Lateral erect if requested. Side bending if requested. Extremities: • Hand, foot, ankle: AP or PA, oblique, lateral. • Evaluation of Congenital Anomaly (Clubfoot) (Newborn or older child) • Standard AP and LATERAL views of both feet. • Supplemental standing views -AP and LATERAL

Childs Skull Xray Image Image & Photo Bigstock
A skull X-ray is typically done after a traumatic head injury. The X-ray allows your doctor to inspect any damage from the injury. Other reasons you may undergo a skull X-ray include.
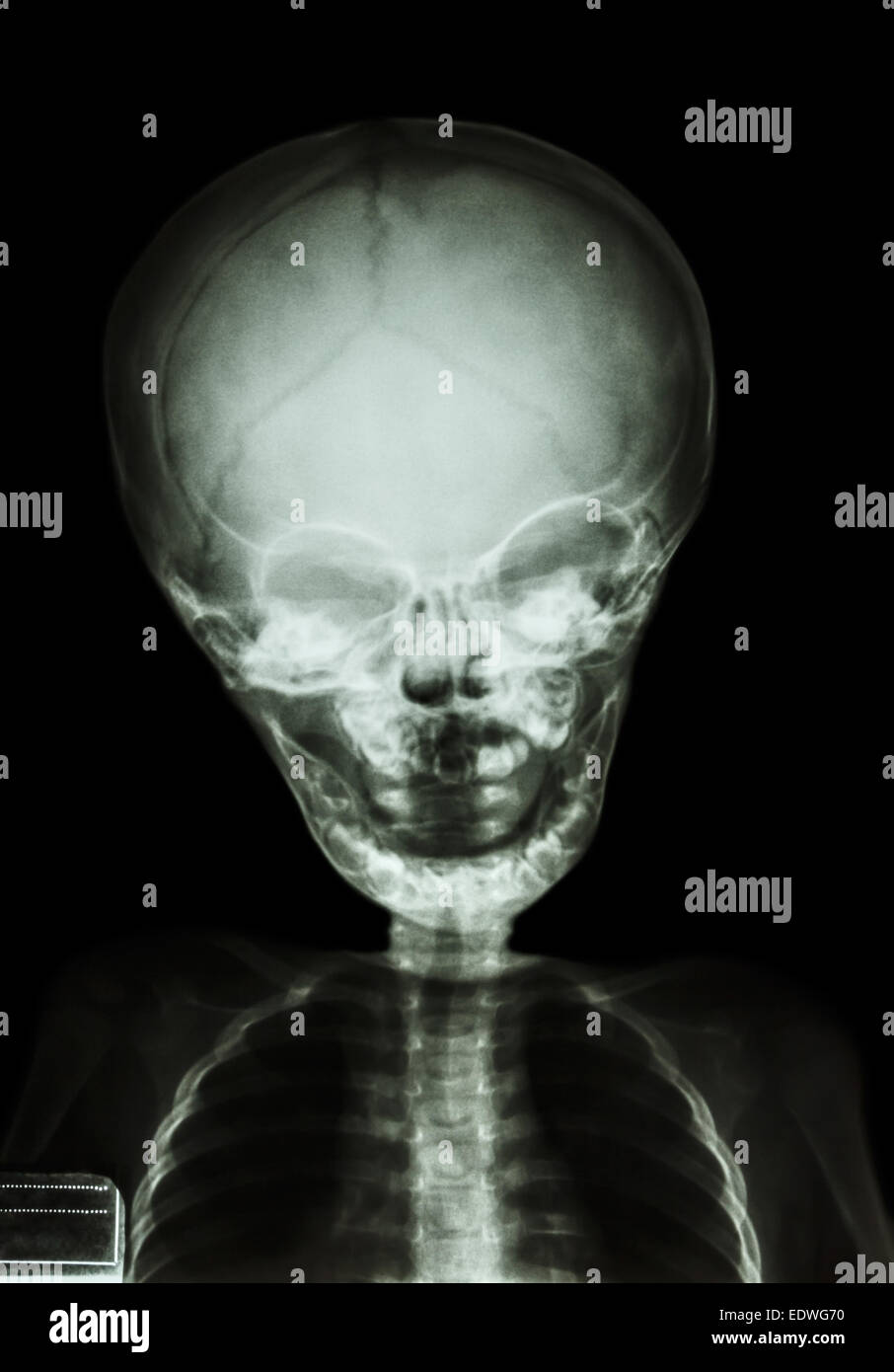
Infant skull hires stock photography and images Alamy
But a baby x-ray is a quick and painless way to obtain important imaging of your infant's body. While radiation exposure is a part of x-ray technology, an occasional x-ray is deemed safe for babies. This helpful tool can quickly determine the cause of sickness, injury or pain, which can outweigh any risks related to the procedure.